Today marks the opening plenary session of SNMMI 2025 and the Henry N. Wagner, Jr., MD Lecture. Cathy Sue Cutler, PhD, FSNMMI, delivered the opening speech under the theme "Accelerating the Cure", providing a comprehensive review of field breakthroughs, analyzing challenges, and outlining the future blueprint for nuclear medicine and theranostics.

Golden Era of Development: High Innovation and Industry Momentum
Cathy Cutler emphasized that nuclear medicine is experiencing a historic golden age: the number of agents in clinical trials has exceeded 250, and for the first time, a nuclear medicine drug advertisement aired during the Super Bowl, signaling a significant boost in public awareness and industry influence. More excitingly, the deep integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with nuclear medicine is revolutionizing not only image analysis and treatment design but also driving targeted drug development into "previously unaddressed disease areas," opening new frontiers for precision medicine.
Challenges and Solutions: A Holistic Approach from Supply Chains to Talent Development
Facing the field's rapid growth, Cathy Cutler addressed three core challenges:
●Workforce and Training Gaps: Collaborative efforts with universities and innovative training models are needed to build a talent pipeline, avoiding "skill shortages" when new technologies are implemented.
●Isotope Supply Chain Risks: The U.S. relies heavily on imported isotopes (30 of which are solely supplied from outside the country), with tariffs and cross-border transportation costs inflating drug prices. A resilient domestic supply chain is urgently needed.
●Patient Access Barriers: Scarce medical resources in community and underserved areas require technical standardization and policy collaboration to optimize resource allocation.
To address these, SNMMI hosted its first Theranostics Summit in May 2025, uniting industry and academia to propose the vision of "identifying a target for every human disease and developing an effective therapeutic solution". Five strategic priorities were established: expanding the workforce pipeline, establishing data-driven best practices, upgrading infrastructure, enhancing theranostics awareness, and resolving funding and reimbursement challenges.
Theranostics Integration: End-to-End Innovation from Lab to Clinic
The speech highlighted cutting-edge advancements in theranostics:
●Technical Breakthroughs: Radiopharmaceuticals like 177Lu-PSMA have demonstrated significant efficacy in prostate cancer treatment, while 225Ac-labeled α-therapies are extending to early tumor intervention.
●Cross-Disciplinary Expansion: Applications are expanding from prostate and neuroendocrine tumors to new frontiers such as Alzheimer's neuroimaging and cardiac functional imaging.
●Combination Therapy Trends: Radiopharmaceuticals combined with immunotherapy, DNA repair inhibitors, etc., enhance efficacy through the "bystander effect," with some clinical trials confirming prolonged progression-free survival.
Additionally, the "MA Shot" raised $2.7 million this year (cumulatively $6 million), earmarked for high-risk, high-reward research to accelerate the "last mile" of translating nuclear medicine technologies from the lab to the clinic.
Global Perspective: From Policy Advocacy to Grassroots Empowerment
Cathy Cutler emphasized the importance of global collaboration: advocating for the WHO to adopt a nuclear medicine capacity-building plan, requiring countries to integrate nuclear medicine infrastructure and workforce training into national healthcare strategies; and launching science outreach in high schools to cultivate industry awareness among youth. "Every $1 invested in nuclear medicine imaging yields over $100 in health economic returns," she stated, calling for policy lobbying and public education to ensure nuclear medicine technologies benefit more patients.
"The future of the field is not distant but lies in every step of collaboration today," Cathy Cutler concluded, urging academia and industry to join forces with the resolve of a "Mars Shot" to accelerate cures and improve patient survival and quality of life. The annual meeting will continue to explore the boundless possibilities of nuclear medicine through 17 therapeutic sessions, new technology exhibitions, and more.
Next came the highly anticipated Henry N. Wagner, Jr., MD Lectureship, delivered by Andrew Scott, MD, from Austin Hospital. As a global nuclear medicine authority, he centered his speech on "Advancing Theranostics Globally", unveiling opportunities and challenges in global nuclear medicine development. This keynote not only outlined the cutting-edge progress of radiopharmaceutical therapy but also systematically stated the end-to-end innovation pathway from technical breakthroughs to policy implementation for the first time.

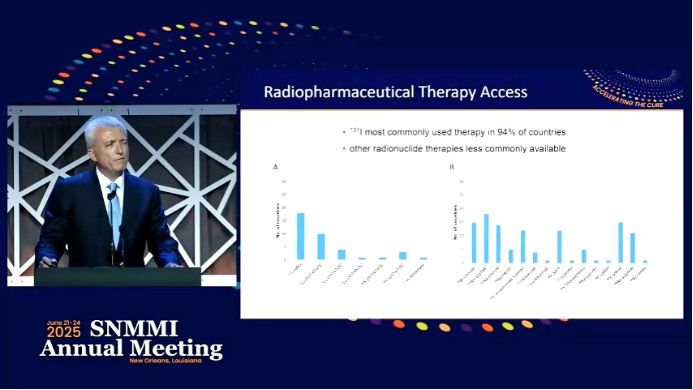
Global Nuclear Medicine Resource Distribution: The 30% vs. 70% Divide
Andrew Scott pointed out that while nuclear medicine is widely applied globally, only about 30% of countries have complete nuclear medicine facilities, with low- and middle-income countries particularly dependent on basic treatment methods. Traditional nuclear medicine research anchored by 99mTc covers over 10,000 hospitals, but theranostics-integrated PET technologies and radiopharmaceutical supply chains remain highly concentrated in high-income regions.

Data shows that I-131, a cornerstone for thyroid disease treatment, is widely accessible in most countries, but novel therapies like 177Lu-Dotatate and PSMA-targeted treatments are routinely applied in fewer than 20% of nations. This resource mismatch directly results in only 1/3 of the approximately 30,000 eligible prostate cancer patients in the U.S. receiving timely 177Lu-PSMA treatment annually, with a far more significant gap globally.
Technological Iteration and Market Explosion: Therapeutic Upgrades from β to α
The speech focused on three breakthrough directions in radiopharmaceutical therapy:
●Isotope and Target Innovation: The early-treatment approval of 177Lu-PSMA for metastatic prostate cancer (FDA March 2025) pushes theranostics toward "first-line intervention"; 225Ac-labeled α-therapies demonstrate higher tumor-killing efficiency in neuroendocrine tumors, complementing β-therapies.
●Combination Therapy Paradigms: The ENZAMET study confirmed that enzalutamide combined with 177Lu-PSMA extends progression-free survival by 40%, while the combination of DNA repair inhibitor NU7441 with 177Lu-DOTATOC halves the effective drug dose, offering new insights for reducing side effects.
●FAP Target Revival: Breakthroughs in fibroblast activation protein (FAP)-targeted molecules for multi-tumor imaging have driven the launch of over 20 clinical trials, including CHAPTER-286, with the related drug market expected to exceed $20 billion by 2030.

From Academic Trials to WHO Policy: The Path to Global Collaboration
Facing challenges like supply chain dependency and workforce gaps, Andrew Scott presented a three-pronged solution:
1、Australian Radiopharmaceutical Trials Network (ART-NET) Model: Standardized processes such as camera credentialing and real-time dosimetry review facilitate cross-disciplinary research, including 600-case FDG PET infection imaging.
2、The Lancet Commission Initiative: Modeling shows that improving nuclear medicine access in low- and middle-income countries could save 10 million lives within 10 years, with every $1 invested in imaging yielding over $100 in health economic returns.
3、WHO Resolution Implementation: The "Strengthening Medical Imaging Capacity" resolution adopted in May 2025 requires countries to report nuclear medicine infrastructure progress every two years, with the IAEA joining SNMMI to launch a global workforce training program.

Future Outlook: The 48-Hour Journey from Lab to Patient Bedside
"We are witnessing the metamorphosis of nuclear medicine from a 'diagnostic tool' to a 'cure engine’, "said Dr. Andrew Scott, citing the VIOLET study of 161Tb-labeled PSMA ligands, which showed significant antitumor activity in 30 cases of refractory prostate cancer, heralding the imminent realization of a precision theranostic closed loop of "imaging-dose calculation-treatment" within 48 hours. With WHO policy support and the "MA Shot" $100 million innovation fund, nuclear medicine is poised to become a standard option in global cancer treatment by 2030.
This lecture not only revised industry growth expectations for radiopharmaceuticals but also provided global nuclear medicine practitioners with a practical guide from technology development to policy advocacy through a three-dimensional framework of "accessibility-efficacy-economy."

After two visionary keynote speeches outlining the global landscape and technological frontiers of nuclear medicine, the annual meeting atmosphere shifted to honor annual excellence. As Dr. Andrew Scott’s discourse on global nuclear medicine resource gaps still lingered in the venue, the footsteps of the award presenters took the stage, artfully bridging the narrative transition from macro strategy to micro breakthroughs, thus kicking off a honor ceremony that blends technological innovation with talent recognition.
Awards Ceremony
SNMMI Henry N. Wagner, Jr., MD Abstract of the Year
Research Title: Quantification of Myocardial Flow Reserve using Exercise Stress F-18-Flurpiridaz PET Imaging


Research Summary: A newly developed cardiac positron emission tomography (PET) imaging technology offers a simpler method for detecting severe coronary artery disease (CAD)—eliminating the need for complex scanning protocols. This innovative approach maintains high diagnostic accuracy while promising to make advanced cardiac imaging more accessible, especially for exercise stress testing scenarios.
Awarded Institutions: University of Ottawa Heart Institute, Alberta Heart Institute, and University of California, Los Angeles
Award Representative: Robert de Kemp, PhD, PEng, PPhys
2025 ERF-SNMMI Paul C. Aebersold Award
Recipient: Julie C. Price, PhD (Professor of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School)


Key Achievements: Dr. Julie C. Price’s kinetic modeling breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s amyloid imaging transformed complex PET analysis into clinical practical tools, perfectly embodying the core philosophy of "technological innovation serving patients."
2025 George Charles de Hevesy Award
Recipient: Wynn Volkert (Professor of Chemistry, University of Missouri)


Key Achievements: With experience in developing 22 radiopharmaceuticals, Dr. Wynn Volkert has charted the evolutionary history of nuclear medicine from diagnosis to treatment—from 99mTc brain imaging agents to 177Lu-PSMA therapy. His developed drug Quadramet has become a vital support for bone metastasis treatment in low- and middle-income countries, deeply resonating with the "global health equity" theme in Dr. Andrew Scott’s report.